The Gupta Empire is widely regarded as India’s Golden Age. Although it existed for only about 230 years (from the 3rd century AD to 543 AD), it had a profound influence on many areas of Indian society, including arts and science. The empire was established by Sri Gupta who came from the Vaishya caste, a low caste within the stratified social class hierarchical system. That said, many of the more remarkable accomplishments that Gupta rulers achieved were chronicled in distinguished texts such as the Allahabad Pillar writings and the Mehrauli Iron Pillar inscriptions.
How Did the Gupta Economy Grow?

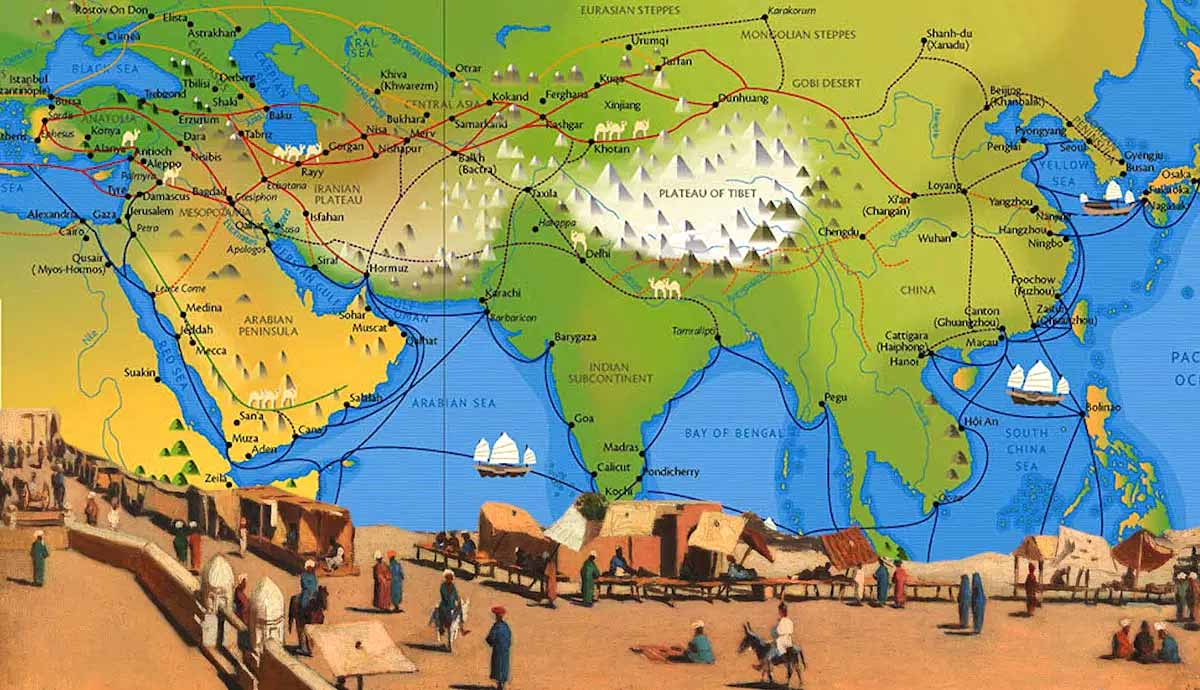
The Gupta Empire’s economy flourished and was mostly based on agriculture and trade. Back then, popular Indian trade items such as spices and valuable metals were traded along the Silk Road and in faraway places like the Roman Empire. The empire’s huge trade network not only made India’s economy better, it also helped to make the culture more diverse.
When it came to the official currency, the Gupta Empire used many different types of coins made from varied valuable metals like gold and silver, all with clear inscriptions. The empire’s gold coins called dinaras, for example, often depicted the ruling emperor or popular gods such as the goddess Lakshmi. The silver and copper coins, on the other hand, often had symbols of the empire.
How Did the Gupta Empire Contribute to Mathematics?

During the Gupta Empire period, polymaths made some major discoveries in areas like mathematics. Among the most noteworthy contributions was the decimal system of notation. Based on the idea of the place value of the first nine numbers, the system relied on the use of zero. The old Indian empire also saw geometry develop.
However, among the most appreciated mathematical discoveries of the time was contributed by Aryabhatta. In 499 AD, he wrote the Aryabhattiyam which covered general mathematics, geometry, and algebra. The period also saw trigonometry solutions advance. It is said that during this period, Indian mathematicians surpassed the Greeks in mathematics.
What Advances Were Made in Astronomy, Literature and Arts During the Era?

Major advances were made in astronomy during the Gupta Empire with eminent astronomers like Varahamihira and Aryabhata making important findings. Aryabhata, for example, discovered that the moon goes between the Earth and the Sun during eclipses. The Panchasiddhantika text written by Varahamihira also changed how people perceived the movement of the stars and the planets by providing a unique approach to the nature of celestial movements. In addition, Gupta astronomers found seven planets in the solar system which was an amazing discovery at the time.
Literature and arts were also openly supported by Gupta rulers and this led to a cultural rebirth that helped shape classical Indian drama and literature. Kalidasa, one of India’s greatest literary figures, wrote his famous works like Shakuntala during this period. The text is said to have captivated Johann von Goethe, the famous German polymath and statesman, several centuries later.
In What Ways Was the Gupta Culture Unique?

The Gupta dynasty successfully ruled a large part of northern India for over a hundred years. When it came to social classes, the Gupta Empire kept the old Varna social class system which consisted of the Brahmins, Vaishyas, Kshatriyas, and Shudras. However, women’s jobs changed during this time with some women getting an education and others rising to leadership roles such as Prabhavatigupta. Prabhavatigupta ruled the Vakataka Dynasty from 390 to 410 following the death of her husband. That said, the majority of women worked in less prominent roles.
In regards to religion, the Gupta society supported Hinduism while accepting other ways of life. Gupta Buddhist art, for example, was prevalent in East and Southeast Asia as trade between the two regions grew. The empire was, at the time, a huge cultural hub whose influence spread to territories such as Sri Lanka, Burma, and Southeast Asia.
Fa Xian, a Buddhist monk and one of the first Chinese visitors to visit India during the rule of Gupta ruler Chandragupta II wrote down notes about the empire. He noted that many Indians were of very high virtues. Xian also observed that the society was quite liberal and that a huge proportion of the population was vegetarian. He additionally shared that the rulers were incredibly lenient when it came to the penal code and offences were mostly punished by fines.